What is obesity prevention

Obesity Prevention Strategies

Turning Around the Epidemic
The fact that the obesity epidemic didnt flash over countries like a wildfire-rather it smoldered and then slowly grew year after year-has made it even more difficult to combat, since its causes have become so intertwined into the social, environmental, and governmental fabric.
Yet efforts to combat obesity-primarily through prevention-are beginning to gain traction, if by a step at a time. To realize real strides, though, positive change must come to all parts of society: from governments and schools, businesses and non-profit organization, neighborhoods and communities, individuals and families. We need to change policies and create an environment where the default option is the healthy choice.
Evidence shows that obesity prevention policy and environmental change efforts should focus on facilitating a handful of key behaviors:
- This section of the website summarizes promising strategies for obesity prevention, based on a review of expert guidance from major governmental, professional, and public health advocacy organizations. Inside, you will find high-level recommendations for changes in key settings-families, early childcare, schools, worksites, healthcare organizations-and for broad, community-wide changes in the food and activity environments that can help make healthy choices easier choices, for all. Each page also includes links to toolkits, guidelines, and other useful resources for putting these obesity prevention strategies into practice. Over time, we will add new obesity prevention strategies, recommendations, and resources as more evidence emerges. Keep in mind that these obesity prevention recommendations are based primarily on a review of U.S. expert guidance, unless otherwise indicated; in other countries, different policy approaches may be needed to achieve improvements in food and physical activity environments.Choosing healthier foods (whole grains, fruits and vegetables, healthy fats and protein sources) and beverages
- Limiting unhealthy foods (refined grains and sweets, potatoes, red meat, processed meat) and beverages (sugary drinks)
- Increasing physical activity
- Limiting television time, screen time, and other sit time
- Improving sleep
- Reducing stress
Overweight and Obesity Prevention
You and your child should each see a healthcare provider once a year to monitor changes in body mass index (BMI). Your provider or your childs pediatrician may recommend lifestyle changes if BMI regularly increases. This is to prevent you or your child from developing overweight or obesity.
What factors contribute to a healthy or unhealthy weight?
Many factors can contribute to a persons weight. These include your:
- Behavior or lifestyle habits, such as lack of physical activity, sedentary behaviors, a poor diet, and poor sleep habits
- Environment, such as where you live and the lifestyle habits within your family
- Economic factors that can influence the foods that you can afford and other lifestyle habits
- Family history and genetic
- Metabolism (the way your body converts food into energy)
Additionally, people from communities with fewer resources, who have food insecurity, or who face other similar issues tend to have a higher risk of developing obesity. NHLBI-funded research found that unhealthy lifestyle habits can worsen the risk of obesity in people who have a genetic risk of obesity. You cannot change some of these factors; for example, the genes you inherit from your parents that determine how tall you are. But you can replace unhealthy habits with healthy ones.
Learn more about our research on obesity.
What Can Be Done
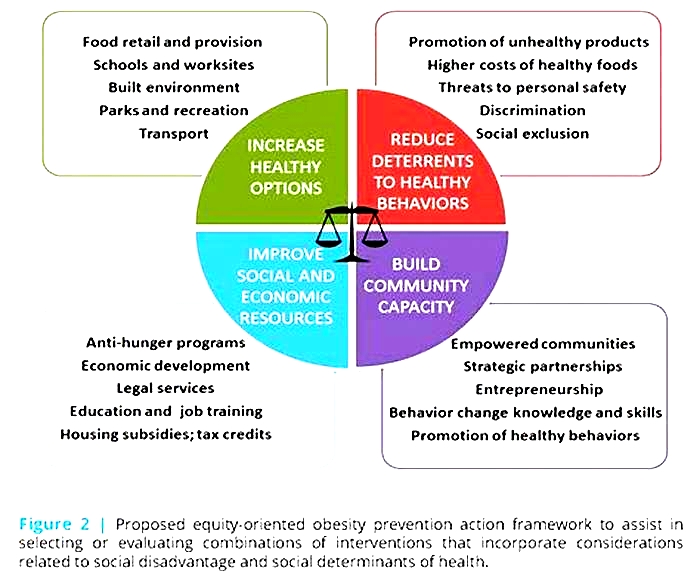
Obesity is a complex disease with many contributing factors. Neighborhood design, access to healthy, affordable foods and beverages, and access to safe and convenient places for physical activity can all impact obesity. Racial and ethnic disparities in obesity underscore the need to address social determinants of health such as poverty, education, and housing to remove barriers to health. Equitable access to obesity prevention and treatment is also needed to slow the obesity epidemic. Policy makers and community leaders can work to ensure that their communities, environments, and systems support a healthy, active lifestyle for all.
The Federal government is
- Studying what works in communities to make it easier for people to be more physically active and have a healthier diet.
- Measuring trends in obesity and related risk factors.
- Developing and promoting guidelines on dietary patternsand amounts of physical activity Americans need for good health.
- Helping families with lower incomes get affordable, nutritious foodsthrough programs such as the Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), Pandemic Electronic Benefit Transfer, and farm-to-education programs.
- Supporting children and families who are at higher risk for obesity through services at Federally Qualified Health Centers, Head Start, WIC, and other service agencies.
- Funding programs and providing training and resources for initiatives that support breastfeeding, promote healthy eating, food and nutrition security, and physical activity.
Some states and communities are
- Making it easier to choose healthy food options where people live, work, learn, and play.
- Making healthy foods more available by connecting local producers with retailers and organizations such as childcare, schools, hospitals, and food hubs.
- Promoting nutrition standards in early care and education settings, food pantries, and faith-based organizations.
- Partnering with business and civic leaders to plan and carry-out local, culturally tailored interventions to address poor nutrition, and physical inactivity and tobacco use.
- Designing communities that connect sidewalks, bicycle routes, and public transportation with homes, early care and education settings, schools, parks, and workplaces.
Healthcare providers can
- Measure patients weight, height, and body mass index, and counsel them on keeping a healthy weight and its role in disease prevention.
- Screen children and adults for overweight and obesity and refer patients with obesity to intensive programs, including family healthy weight programs and the Diabetes Prevention Program.
- Counsel patients about nutrition, physical activity, and optimal sleep.
- Use respectful and non-stigmatizing, person-first language with all individuals in weight-related discussions.
- Connect patients and families with community services to help them have easier access to healthy food and ways to be active.
- Discuss the use of medications and other treatments for excess weight.
- Seek out continuing medical education on the latest on obesity science.
Everyone can
- Eat a healthy diet by following the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
- Get the amount of physical activity recommended by the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd edition.
- Get involved in community efforts to improve options for healthier foods and physical activity.
- Lose weight, if they weigh more than recommended, to help reduce risk for many chronic diseases.
- Get enough sleep.
- Manage stress.
- Talk to their healthcare providers about available obesity prevention and treatment options to help reduce potential health risks.
How to Prevent Obesity in Kids and Adults
Obesity is a common health issue that is defined by having a high percentage of body fat. A body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher is an indicator of obesity.
Over the last few decades, obesity has become a considerable health problem. In fact, its now considered to be an epidemic in the United States.
According to statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), roughly
Despite the rising percentages, there are plenty of ways to prevent obesity in both kids and adults. Here well explore both, as well as how far weve come in preventing obesity.
Obesity prevention begins at a young age. Its important to help young people maintain a healthy weight without focusing on the scale.
Breastfeed infants, when possible
One
Feed growing children appropriate portion sizes
The American Academy of Pediatrics explains that toddlers dont require huge amounts of food. From ages 1 to 3, every inch of height should equate to roughly 40 calories of food intake.
Encourage older children to learn what various portion sizes look like.
Build early relationships with healthy foods
Encourage your child to try a variety of different fruits, vegetables, and proteins from an early age. As they grow older, they may be more likely to incorporate these healthy foods into their own diet.
Eat healthy foods as a family
Changing eating habits as a family allows children to experience healthy eating early on. This will make it easier for them to continue following good eating habits as they grow into adults.
Encourage eating slowly and only when hungry
Overeating can happen if you eat when youre not hungry. This excess fuel eventually becomes stored as body fat and can lead to obesity. Encourage your child to eat only when they feel hungry and to chew more slowly for better digestion.
Limit unhealthy foods in the household
If you bring unhealthy foods into the household, your child may be more likely to eat them. Try to stock the fridge and pantry with healthy foods, and allow less-healthy snacks as a rare treat instead.
Incorporate fun and exciting physical activity
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that kids and teens get at least
Limit your childs screen time
More time spent sitting in front of a screen means less time for physical activity and good sleep. Because exercise and sleep play a role in a healthy weight, its important to encourage those activities over computer or TV time.
Make sure everyone is getting enough sleep
Research suggests that both
Know what your child is eating outside of the home
Whether in school, with friends, or while being babysat, children have plenty of opportunities to eat unhealthy foods outside of the home. You cant always be there to monitor what they eat, but asking questions can help.
Many of these obesity prevention tips are the same for losing or maintaining a healthy weight. The bottom is line that eating a healthy diet and getting more physical activity can help prevent obesity.
Consume less bad fat and more good fat
Contrary to the belief behind the low-fat diet craze of the 90s, not all fat is bad.
Consume less processed and sugary foods
According to a
Eat more servings of vegetables and fruits
The daily recommendation for fruit and vegetable intake is five to nine servings per day for adults. Filling your plate with veggies and fruit can help keep calories reasonable and reduce the risk of overeating.
Eat plenty of dietary fiber
Studies continue to show that dietary fiber plays a role in weight maintenance. One
Focus on eating lowglycemic index foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale used to measure how quickly a food item will raise your blood sugar. Focusing on low-GI foods can help keep blood sugar levels steadier. Keeping your blood glucose levels steady can help with weight management.
Get the family involved in your journey
Social support isnt just for children and teens its important for adults to feel supported too. Whether cooking with family or going on walks with friends, getting people involved can help to encourage a healthy lifestyle.
Engage in regular aerobic activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into your schedule is important for maintaining or losing weight, among other benefits. The
Incorporate a weight training regimen
Weight training is just as important to weight maintenance as aerobic activity. In addition to weekly aerobic activity, the WHO recommends weight training that involves all your major muscles at least two times per week.
Focus on reducing daily stress
Stress can have many effects on the body and mind. A
Learn how to food budget and meal prep
Its much easier to grocery shop for healthy foods when you have a plan. Creating a food budget and list for your shopping trips can help avoid temptations for unhealthy foods. In addition, prepping meals can allow you to have ready-to-go healthy meals.
Preventing obesity plays an important role in good health. Obesity is associated with a long list of chronic health conditions, many of which become more difficult to treat over time. These conditions include:
By focusing on obesity prevention and lifestyle changes, it may be possible to slow or prevent the development of these diseases.
Although the research on obesity prevention strategies is limited in the United States, international studies have been able to suggest some answers.
A
However, a
A
Preventing obesity in adults involves regular physical activity, a decrease in saturated fat intake, a decrease in sugar consumption, and an increase in fruit and vegetable consumption. In addition, family and healthcare professional involvement may help to maintain a healthy weight.
One
However, only some of these methods have proven to be effective, and there are barriers to using these methods.
A healthy weight is important in maintaining good health. Taking steps to prevent obesity in your daily life is a good first step. Even small changes, such as eating more vegetables and visiting the gym a few times a week, can help to prevent obesity.
If youre interested in a more tailored approach to your diet, a dietitian or nutritionist can provide you with the tools to get started.
Additionally, meeting with a personal trainer or fitness instructor can help you find the physical activities that work best for your body.