What foods are too fatty for dogs

Which Fats Are Healthy For Dogs?
Unlike its nutritional siblings protein and fiber, fat doesnt get much good press in the pet food world. Theres an obvious reason for this feed your dog too much fatty food and you risk them becoming obese, a condition that can lead to a ton of nasty health conditions.
However, that doesnt mean you should race out of the house and stock up on fat-free dog food. Thats because not all fats are created equal and some varieties can be good for your pet indeed, some are essential to life.
Healthy fats and oils are a great energy source for active, happy pups, says Bridget Meadows, Director of Food Engineering at Ollie. It helps them to fuel their muscles and absorb important vitamins and minerals. Dogs also need fat in their diet to stay visibly healthy a dog with good fat in their diet has enough energy to play, healthy skin, and a shiny coat.
As well as that, healthy fats can aid with the following:
- Cell development
- Neurological function
- Hormone production
- Reproductive support
- Inflammation reduction
What are the good types of fat?
So which fats should parents look for in dog food to get these effects? There are two big ones.
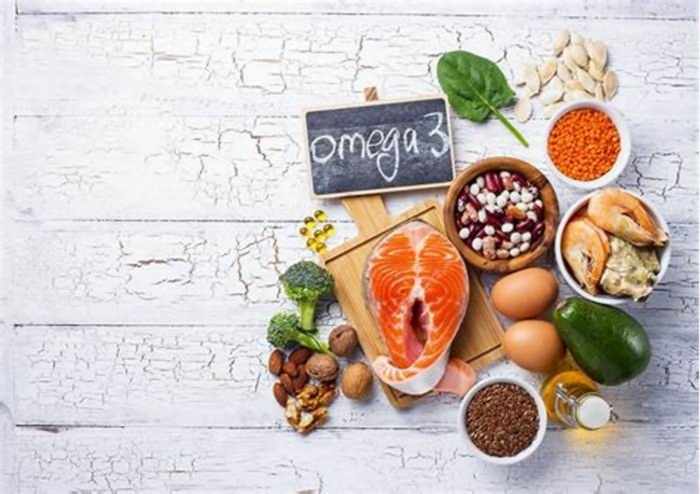
Omega-3 fatty acids
You might already be familiar with Omega-3 fatty acids from their inclusion in human food products. They tend to make their way into dog food recipes via ingredients recognizable to parents, such as flaxseeds, fish oils and canola.
There are several different types of Omega-3s to be aware of, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Sometimes, pet food ingredients on the back of the packaging will be described as being enriched by one of these.
Omega 3 fatty acids like DHA are especially important for the development of puppies, including the growth and health of their brain and eye function, says Meadows. Added to that, Omega-3s can help with your dogs hearing and strengthen their nervous system.
At the other end of the scale, your pet runs the risk of suffering from depression, poor memory and learning ability, or declining sight and hearing if they dont have enough Omega-3s in their diet.
Omega-6 fatty acids
Despite the name, these arent doubly as good as Omega-3s the number refers to the position of the first double bond in the hydrocarbon chain. Essentially, theyre similar, but different.
For a start, Omega-6s are derived from different sources, such as animal fat, sunflower oil or coconut oil.
And while Omega-6s also contribute towards healthy brain function, they also play an important role in ensuring optimal growth, immune function and reproductive support.
Without enough Omega-6s in their diets, dogs run the possibility of suffering from unhealthy weight loss, impaired growth, hair loss, skin conditions and increased chances of infections.
How can I ensure my dogs getting enough Omega fatty acids?
No mammal is capable of synthesizing their own supply of Omega-3 or Omega-6 fatty acids, so theyre dependent on getting them from their food.
Be sure to look at the ingredient list of pet food before you serve it up to your dog and look out for the ingredients listed above.
Alternatively, puppy food that meets the AAFCOs Nutrient Profile for Growth & Maintenance should include the minimum amount of ALA, EPA and DHA as recommended by the organization.
However, theres no minimum amount required in food labeled as Adult Maintenance, although theres a maximum ratio of Omega-6s to Omega-3s permitted, which is 30:1.1
If youre concerned the food youre serving to your dog is lacking in Omega-3s or 6s, you can search for recipes including ingredients rich in fatty acids or ask your vet about the possibility of giving your pet dietary supplements.
A guide to DHA for dogs
Many studies have proven the benefits of giving DHA supplements to dogs to lower their risk of developing certain health conditions including osteoarthritis, cardiovascular diseaseTrusted SourcePubMed CentralArchive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature.Go to source, and various types of cancer. Other benefits of DHA include:
Reduced allergic reactions. Fatty acids such as DHA and, to a lesser degree, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) have anti-inflammatory properties that can help to soothe allergy symptoms in dogs, especially those caused by immunodeficiencies.
Improved brain health. DHA is essential for healthy cognitive function in dogs. The correct amount of DHA in a dogs diet can improve memory, attention span, and trainability. It may also help to control the symptoms associated with brain aging in older dogs, including canine cognitive dysfunction and dog dementia.
Healthier vision. DHA plays a vital role in developing the light-sensitive lining at the back of the eye that sends messages to your brain to enable you to see.
A shinier coat. For dull dog coats, consider adding a DHA supplement to their diet to improve coat health and maintain a healthy sheen. Fatty acid supplements may also help with hair loss, depending on the cause.
A more robust immune system. The immune system protects your dog from invading pathogens and bacteria that can cause illness and disease. DHA boosts your dogs immune system, increasing antibody production to improve immune response.
Reduced inflammation. The increase in antibody production caused by DHA can also help with inflammation. Some studies have shown a link between DHA and a lower risk of heart diseaseTrusted SourceCummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts UniversityVeterinary school.Go to source because of its ability to decrease the effects of pro-inflammatory proteins, reducing pain and swelling.
A healthier central nervous system. DHA is the most common fatty acid found in canine brains, accounting for 30% of the fat in the brains gray matter. Its essential for optimum brain function and the development of the central nervous system in puppies. Its especially important for nerve cell structure, which regulates vital body functions such as digestion and the effective pumping of the heart.
Improved joint health. Veterinarians estimate that 20% of all dogsTrusted SourcePubMed CentralArchive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature.Go to source over the age of 1 suffer from some osteoarthritis. Common causes include hip dysplasia, an injury, and obesity. Supplements that contain DHA and EPA can aid cartilage development which helps protect the joints from damage. However, remember that regular exercise is still the best way to keep your dogs joints healthy.
This Dangerous Health Problem Happens to Dogs on a Fatty Diet
Youre cooking a big meal for your family filled with indulgent foods like a roasted turkey, buttered biscuits and decadent gravy. Your furry friend is underfoot in the kitchen, giving you their best puppy-dog eyes while they beg, and you cave. Giving your dog a healthy chunk of meat and flavorful skin cant hurt, right?
Unfortunately, its these kinds of situations that might land dogs in the emergency veterinarian with a dangerous health problem. Many pet parents are unaware of an issue called pancreatitisand how seemingly innocent gifts like the one above can cause it.
What is pancreatitis?
At the most basic level, pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. Although its well-known that inflammation can be dangerous for dogs in the long term, the inflammation caused by this condition can be life-threatening, and its not always easy to spot when it occurs.
The pancreas releases enzymes that help your dog digest food. These enzymes are only supposed to activate when they reach the small intestine, where the bulk of digestion occurs. Unfortunately, if the pancreas becomes inflamed, enzymes are prematurely released from the organ and activated, which leads to the digestion of the pancreas and its surrounding tissues. This process can significantly damage the pancreas and other organs in the abdomen and is usually very painful for the suffering pet.
Without prompt medical treatment, pancreatitis can cause severe organ damage, internal bleeding and even death.
Pancreatitis can either be acute or chronic. Acute pancreatitis comes on suddenly, is usually severe and can be life-threatening if its not caught and inflammation spreads to the surrounding organs. Chronic pancreatitis develops slowly over time and is usually characterized by persistent, low-grade inflammation. Chronic pancreatitis may flare up on occasion, causing more severe symptoms.
But what exactly leads to inflammation of the pancreas? As it turns out, quite a few things could be to blame.
One of the most common causes of pancreatitis in dogs is a fatty diet. The condition could be brought on by feeding your pup a high-fat diet for their daily meals. It might also be brought on if your dog normally eats a low-fat diet and suddenly gets a large serving of fatty food (like being fed table scraps or rummaging through the garbage). Fatty diets raise the amount of fat present in the blood, which can cause pancreatic inflammation. This risk factor is highest in overweight and inactive dogs.

Other things can also cause pancreatic inflammation, including obesity, trauma to the pancreas, hypothyroidism, Cushings disease, certain medications and toxins.
Additionally, because the pancreas is responsible for producing insulin, diabetic dogs may be at a higher risk for pancreatitis. However, damage to the pancreas because of pancreatitis may also increase your dogs risk of diabetes if they do not have the condition already.
Spotting and treating pancreatitis
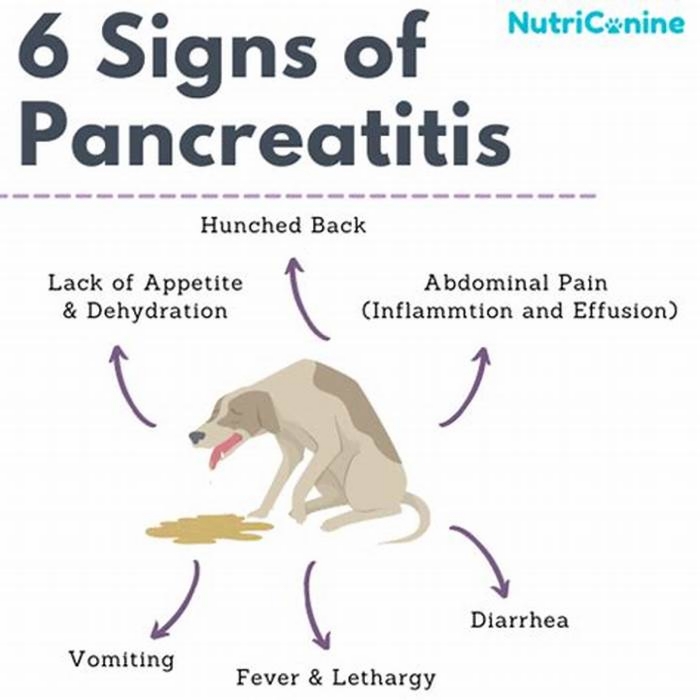
Unfortunately, pancreatitis can look a lot like other, milder health problems in dogs because of their shared symptoms. The following symptoms are the most common:
- Hunched back or bowed posture
- Vomiting repeatedly
- Distended and painful abdomen
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Lethargy
- Inappetence
The most telling symptoms are a painful belly and repeated vomiting. While your dog might vomit once after eating something that doesnt agree with them, multiple bouts of vomiting in a short time period combined with pain in the abdomen are pretty sure signs of pancreatitis.

If you notice signs of pancreatitis in your dog, its very important that you seek veterinary help as soon as possible to ensure your pets comfort and safety. Severe cases of the condition may require testing, IV fluids and monitoring to allow the inflammation to go down.
After immediate treatment, your dog may need long-term management to prevent reoccurrence of the problem, which is often high. This generally includes feeding your pup small meals throughout the day, rather than one or two large ones. Your dog will also need to be put on a strict low-fat dietand absolutely no table scraps should be given!
Dogs with severe or chronic pancreatitis may need to have their diet permanently alteredusually using a prescription ultra-low-fat foodto ensure their safety for the rest of their lives. In more mild cases, your dog may be able to return to their normal diet (if it is low enough in fat) after the condition has cleared.
Pancreatitis prevention
In many cases, pancreatitis is preventable by regulating your pups diet. These three things can go a long way in preventing pancreatic inflammation and the problems that come with it:
- No table scraps: Most dogs eat a diet with an appropriate amount of fat. However, this can cause problems if they suddenly find themselves with a high-fat meal or treat. For this reason, avoid feeding your dog any table scraps that are fatty, such as pieces of meat or foods with lots of butter.
- Feed a low-fat diet: Some store-bought pet foods have high levels of fat that could be detrimental to dogs who dont move much. Discuss your pet food options with your vet to determine whether your dog needs to be fed something with lower levels of fat to reduce their risk for obesity and pancreatitis.
- Maintain their weight: Obese pets have a much higher risk for pancreatitis than active, lean pets. Ensure your pet maintains a healthy weight by exercising with them frequently and potentially switching them to a weight-loss diet.
Prevention is a much better approach to pancreatitis than life-long management of this painful condition. So, ignore the puppy-dog eyes and give your dog a low-fat treat, insteadits good for their health!
Best Omega-3 Rich Food For Dogs
We can read endless features on dietary changes for humans, but many of us don't think the same about our pets. Feeding our dogs commercial dog food is easy and it can be sufficient for the majority of dogs. Even though some of them are marketed as being nutritionally complete, some may be lacking in certain nutrients. While omega-3 fatty acids are great for all dogs, some will need them more than others.
In this AnimalWised article we look at the best omega-3 rich food for dogs. We look at the reasons why dogs need omega-3 fatty acids in their diet and which dogs in particular might benefit from them.
Omega-3 fatty acid benefits for dogs
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential oils which are only available to dogs via their diet. This is to do with how the omega-3 oils are metabolized as nutrients in the body, since they cannot synthesize them on their own. They are referred to as essential fatty acids due to the inability of dogs to manufacture them themselves. Here are the general health benefits omega-3 fatty acids provide for dogs:
- Boost their immune system
- Strengthen joints and reduce chances of arthritis
- Reduce joint pain if they already have arthritis or other joint diseases
- Helps keep the heart healthy
- Helps liver and kidney function
- Improves skin and coat quality
- May help prevent certain cancers
A deficit of omega-3 fatty acids can lead to various health problems in the dog. Some of the most noticeable are those which affect the condition of the dog's skin, hair and nails. Less obvious, but no less serious, problems include joint weakness. Not only are omega-3 fatty acids essential for a dog's well-being, they can also provide specific health benefits to improve their fitness and appearance.
These fatty oils act in a similar way to antioxidants in the body. Although their exact effects are still to be determined, reports show they have a mild anticoagulant effect[1]. This means they can be beneficial in helping to prevent cardiovascular disease. Since they have the potential for positive influences on the dog's cardiovascular system, this makes them especially important for young puppies and senior dogs.
Since the omega-3 fatty acids help to keep a dog's coat and nails healthy, they are beneficial to protect them from the elements. Since a dog's coat and nails are indicators of their general well-being, they should be incorporated into their diet.
There are certain breeds which are believed to have even greater benefit from omega-3 fatty acids. This is because dog breeds such as the Shar Pei, French Bulldog or Pug have folds in their skin which make them prone to diseases such as atopic dermatitis. Essential fatty oils can help keep their skin healthy and avoid such health problems. This is why omega-3 fatty acids should be included in their diet.
Do dogs need omega-3 supplements?
While omega-3 fatty acids are essential for a dog's health and well-being, they may not necessarily need them supplemented in their diet. The reason for this is because the food they eat may already have enough for their nutritional needs. The types of food a dog can eat include:
- Commercial dry dog food
- Commercial wet dog food
- Homemade cooked dog food
- BARF or raw food diet
Of course, it is also possible you may want to give your dog some combination of these different dog food types. A quality dog food, both wet canned food and dry kibble, will have omega-3 fatty acids as part of its formula. However, some less reputable brands may be nutritionally deficient. It will be up to you to check the quality of the food you buy and you can always ask your veterinarian for a recommendation if you are unsure.
With a homemade diet, you will need to ensure their omega-3 fatty acid levels are well-maintained. With a raw food BARF diet, it can be very difficult to give them all the nutrition they need. Raw meat such as chicken and beef does not have high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. For this reason, you will have to include some other omega-3 rich food in their diet or provide them with suitable supplements as recommended by your veterinarian.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids for dogs
While there is some debate, a dog is considered omnivorous with a carnivorous bias. Much of their nutrition comes from animal-protein, but they have also been able to digest other food types thanks to their history of domestication. However, some nutrients such as taurine and vitamin D cannot be synthesized naturally, so they need it in their diet. This is similar to their need for omega-3 rich foods.
Some of the most common omega-3 rich foods are found in the blue fish category. However, there are also vegetables and other foods which can be used in the dog's diet. Foods for dogs high in omega-3 include:
- Salmon: perhaps the most well-known omega-3 rich food, salmon provides many other benefits. Being high in protein, it will also meet many of the dog's other nutritional needs. However, it is not a cheap ingredient and is often prohibitively expensive for many dog owners.
- Sardines: a little cheaper than salmon, sardines are also high in omega-3 fatty acids. They should be eaten fresh as canned sardines often have lots of oil, salt and other ingredients which would be counterproductive to give your dog.
- Anchovies: similar to sardines, these small fish are high in omega-3 and are relatively cheap.
- Linseed: also known as flax, linseed is a non-fish source of omega-3 which can be easily added to your dog's food. Linseed oil is also rich in these fatty acids, so this can be stirred in easily to your dog's food.
- Chia seeds: another great seed which has the benefit of high levels of omega-3. They are often added to commercial dog foods to help boost their nutritional value, but they can also be added to homemade food.
- Soybean: as well as being a legume which is known as having a high protein count, soybeans are also full of omega-3. Edamame is the name for the prepared version of soybeans when cooked, but they too can contain additives which are not beneficial to your dog.
There are other foods for humans which are high in omega-3 fatty acids. They include oysters, walnuts and caviar. However, these are not suitable for practical reasons. Oysters and caviar are prohibitively expensive and walnuts should not be eaten in large amounts as they can cause digestive issues.
However, there are also other ways to supplement omega-3 in your dog's diet. Capsules, oils and tablets can be used, but we need to be careful. Fish oil is a particularly common way of giving it to dogs. Each formulation is different and some may contain other ingredients which are not suitable for canine consumption. For these reasons, before you supplement omega-3 in your dog's diet, we remind you of the importance of consulting a veterinarian.
Can dogs have too much omega-3 fatty acid?
A balanced diet is just that, not too much, not too little. While omega-3 fatty acids are essential for a dog's well-being, we shouldn't go overboard. Some people will add fish oil and other oils to every meal a dog has. An excess of such oil will not be particularly toxic, so the side effects are considered mild.
The problem is that, although many of the omega-3 rich foods have healthy fats, they are still fats. Adding too many to your dog's diet can result in the dog becoming overweight. They can also cause certain gastrointestinal issues which can lead to vomiting, diarrhea and other symptoms.
Omega-6 fatty acids for dogs
While this article is focused on omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids are also very important for your dog's health. Omega-6 fatty acids work in similar ways to omega-3 and have similar health benefits for your dog. They are important for cell structure, growth and repair, meaning they are especially important for developing dogs. However, they need to be of quality and in the right balance to provide benefit to your dog[2].
Foods high in omega-6 fatty acids include:
- Hemp seeds
- peanut butter
- Avocados
- Eggs
- Almonds cashews
However, while these foods are not necessarily toxic to your dog in small amounts, large amounts can be dangerous. Not only can they seriously increase their fat intake, they may also cause gastrointestinal issues. For this reason, commercial food rich in omega-6 fatty acids are usually enough to provide what they need.
If you want to read similar articles to Best Omega-3 Rich Food For Dogs, we recommend you visit our Homemade diets category.
References
1. Sokoa-Wysoczaska, E., et al. (2018). Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Potential Therapeutic Role in Cardiovascular System DisordersA Review. Nutrients, 10(10), 1561.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6213446/
2. Biagi, G., Mordenti, A., & Cocchi, M. (2004). The role of dietary omega-3 and omega-6 essential fatty acids in the nutrition of dogs and cats: A review. Progress in Nutrition, 6(2), 0-0.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272784328_The_role_of_dietary_omega-3_and_omega-6_essential_fatty_acids_in_the_nutrition_of_dogs_and_cats_A_review
Videos related to Best Omega-3 Rich Food For Dogs
Videos related to Best Omega-3 Rich Food For Dogs