Is omega 3 bad for dogs with pancreatitis
Are omega-3 fatty acids safe and effective in acute pancreatitis or sepsis? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Background: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is marked by a strong pro-inflammatory response, which may cause a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), organ failure, and death. Early administration of omega-3 fatty acids (FA) may reduce the pro-inflammatory response and improve outcome in AP. A systematic review focusing on the safety and efficacy of omega-3 FA in AP is lacking.
Aim: Evaluate the safety and efficacy of an intervention with omega-3 FA in acute pancreatitis and additionally in sepsis.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis was performed using the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases including only randomized controlled trials in AP and, for safety endpoints, in sepsis investigating intervention including omega-3 FA without other active components (e.g. addition of glutamine to the intervention). The primary outcome was mortality.
Results: After screening 1186 studies, five randomized trials (n = 229) with omega-3 FA in AP were included. In AP patients treated with omega-3 FA within 48 h after hospitalization, a non-significant reduction of mortality was seen (OR 050, 95%CI 013-199, p = 033), compared to controls. In two studies (n = 85), omega-3 FA reduced the risk of new onset of organ failure (OR 033, 95%CI 012-093, p = 004). Nine randomized trials with 312 patients suffering from sepsis (not pancreatitis related) demonstrated a reduced mortality (OR 052, 95%CI 028-097, p = 004). None of these 14 randomized trials reported safety concerns.
Conclusions: Administration of omega-3 FA could reduce the risk of new-organ failure in patients with AP. There were no safety issues reported of the early administration of omega-3 FA in any of the included studies. To show the real clinical benefit of omega-3 FA in AP, a large and pragmatic randomized controlled trial is needed.
Pancreatitis: Natural Guide for Pets
What does the pancreas do?
The pancreas is a small organ that sits behind the small intestine and the stomach. The pancreas digests food and regulates a cat and dogs blood sugar.
The pancreas produces and stores inactive enzymes that should only be activated when they enter the small intestine. Amylase for carbohydrate digestion, lipase for emulsifying and digesting fats and protease for digesting protein.
Most of the pancreas is composed of cells that produce digestive enzymes. These cells are arranged in clusters that are connected to a series of small ducts. Pancreatic enzymes and juices flow from the cells and minor ducts into the main pancreatic duct, leading to the duodenum. The pancreas also contains small islands of hormone-producing cells called the islets of Langerhans, which secrete insulin and glucagon,along with somatostatin, hormones that mostly regulate blood sugar metabolism.
What is pancreatitis
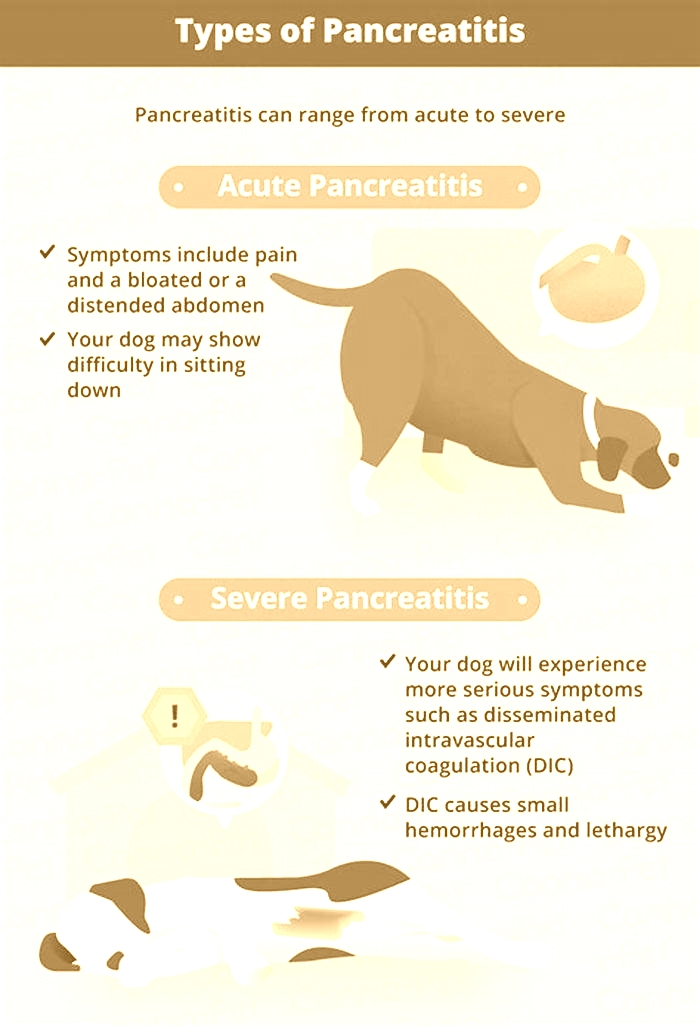
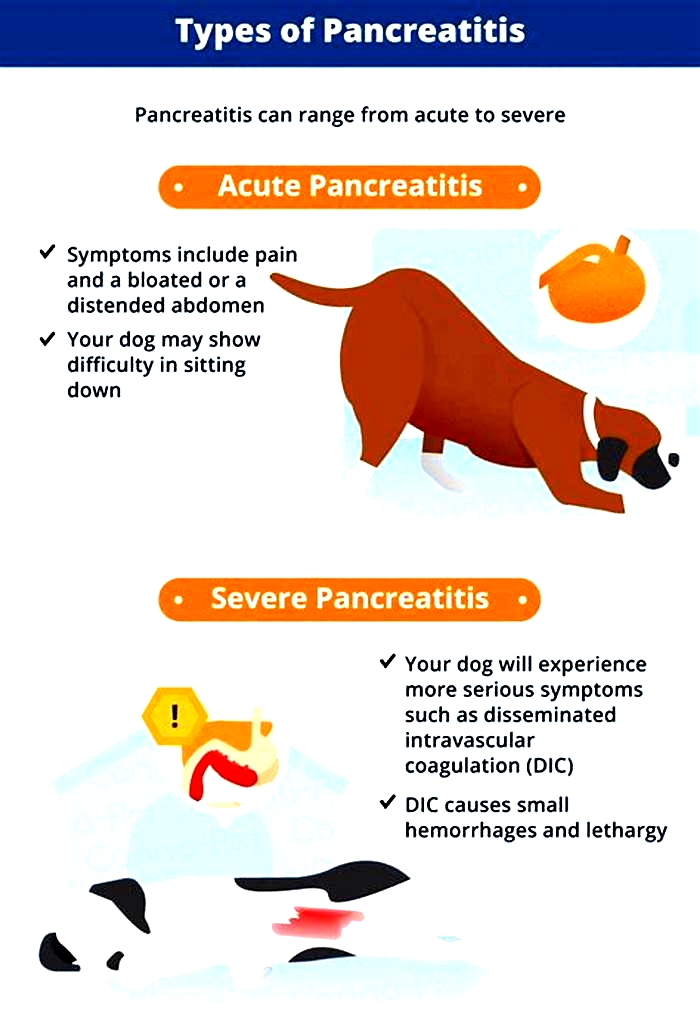
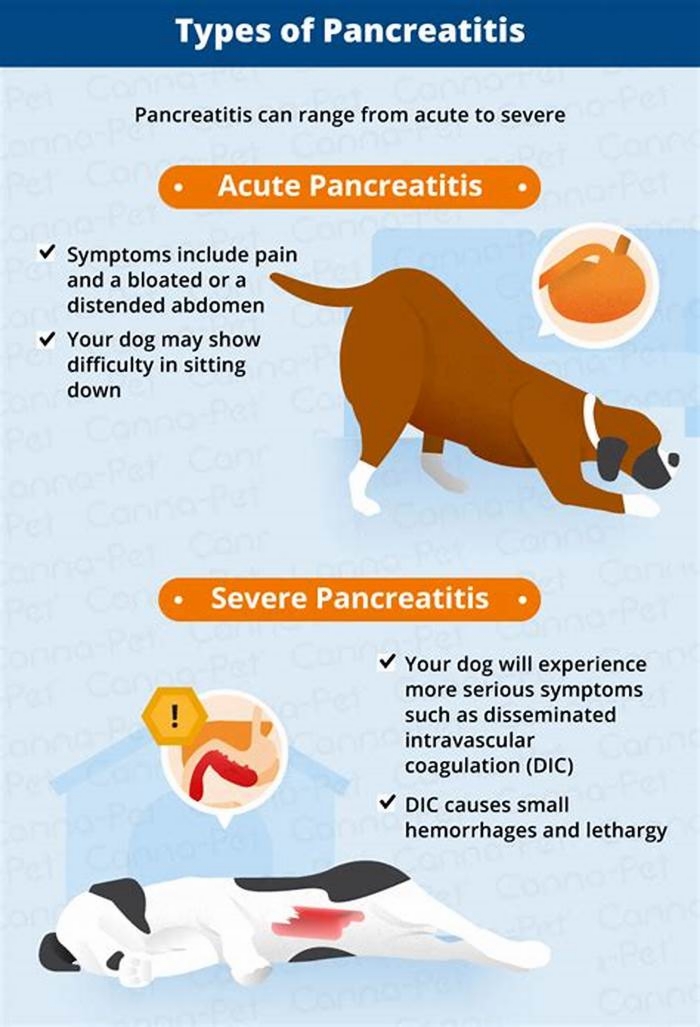
Pancreatitis is the intense inflammation and swelling of the pancreas. It can either be an acute case, where animals can be at high risk (sometimes fatal) from a sudden onset of mass inflammation, where this tends to go away in a matter of a few days to a week (if the patient survives it).
Chronic pancreatitis is a low grade inflammation over an extended period of time, leading to other possible health complications. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the termed coined when the pancreas is no longer able to produce digestive enzymes, this can result from chronic pancreatitis. When the pancreas is damaged, further complications such as diabetes may appear over time, if not managed effectively.
The prognosis depends on the severity of the disease. If left untreated, pancreatitis may lead to severe organ damage and even sudden death. Pancreatitis can cause a lot of pain and damage so if your pet seems uncomfortable, please do not ignore this, go to your veterinarian.
Common symptoms but not exclusive are;
- Loss of appetite
- Sickness
- Diarrhoea
- Lethargy
- Dehydration
- Restlessness
- Arched back
In milder forms, symptoms arent always obvious but may include loss of appetite,lethargy anddiarrhoea. During an attack they may hunch the back, holding their bottom in the air with front legs and head low to the floor.
Why it is so prevalent
It is almost 50% more common in cats and dogs than in humans. A combination of environmental and genetic factors plays a role in the development of many cases of pancreatitis in pets. We see many acquired inflammatory issues related to IBS and IBD.
You will find certain breeds such as cocker spaniels, dachshunds, miniature schnauzers and poodles are more susceptible to pancreatitis due to common genetic snips (SNP) in cats and dogs. Its sometimes difficult to pinpoint the exact cause of pancreatitis but the following definitely play a part in the full picture of health.
- Scavenging; eating spoiled foods and incredibly high amounts of oxidised fat.
- Processed foods;eating processed foods, always high in sugars and sometimes grains are specifically high in carbohydrates.These carbohydrates put an unusual load on the pancreas. Cats and dogs are carnivores and naturally produce less amylase than any other digestive enzyme in the digestive system.
- Rancid fats;found in poor processed foods and poorly stored fats, leading to oxidation and inflammation and therefore, more than likely, leaky gut.
- IBS/IBD; low HCLlevels in the gut, poor microbiome andconstantimmune triggers to environmental stimuli, food being the biggestoffender, seems to be involved in a low grade chronicinflammation that may impact thepancreas and can bring about episodes orundiagnosed characteristics of pancreatitis.
- Grains and Lectins;often contained in dry food due to being cheap ingredients, creates inflammation and up regulates a protein called zonulin. Zonulin is responsible for (and a new diagnostic biomarker of) intestinal permeability (leaky gut).
- Leaky gut/gut integrity/intestinal permeability;leaky gut is when the integrity of the one cell epithelial lining of the gut, becomes compromised by inappropriate foods, allergens, toxins and so forth. These slack and under functioning junctures allow chemicals, including food stuff into the blood stream, that should not be permitted. Leaky gut is linked to many disease states and closely linked to a lowered gut immunity in pancreatitis.
- Inflammation and imbalanced immunity; acute and chronic pancreatitis are dynamic inflammatory processes. Immune cells playa critical role in pancreatitis progression so looking towards that intricate cascade and supporting stress are key.
- Pharmaceuticals; in recent years, a large number of commonly prescribed medications have been linked to drug-induced pancreatitis pathogenesis. Although mechanisms are proposed, the exact cause of injury is not well understood.
- Obesity; obese animals are predisposed to a wide variety of diseases affecting many organ systems. Endocrine disorders commonly associated with obesity include caninepancreatitis.
- Cushings disease; is an endocrine disease and is commonly associated in pancreatitis.
- High blood levels of fats; triglycerides, have also been listed as a risk factor to pancreatitis in canines.
- Infections such as Babesia canis or Leishmania have shown to be present in some canine pancreatic patients.
- Genetics; genetic polymorphisms are found in certain breeds, the most common being SPINK1. Feeding a processed diet and in a toxic environment (vaccinations included), are more likely to express this gene, however this is far too common a disease for it to be purely genetic.
Nutrition regime in pancreatitis
Theres a lot of conflicting advice out there for pancreatitis but we have worked in this with humans and pets and the aetiology, pathogenesis and therefore dietary plans are rather similar in terms of approach and the following can be very helpful.
Findings hereWe do not advocate any processed foods in this disease, only fresh, balanced, home cooked or raw food.
There is often the suggestion that small meals spread over time is the best protocol in pancreatitis but this activates the pancreas, aggravating the inflammation further. When you start feeding fresh and balanced food over time, we find feeding twice a day, if your schedule permits it, feeding breakfast around 9am and then dinner at about 4pm, allowing a longer fast between dinner and the following breakfast. If your pet can tolerate being fed once a day, this might be even better but tread with caution. If your cat or dog is predisposed to the hunger pukes, we suggest feeding later and earlier in the day and perhaps feed 3-4 times a day. Each animal is different and its important to figure out what suits your pet best.
15% dry matter (DM) fat content (usually around 5% crude fat), is usually recommended for dogs with acute and chronic pancreatitis. We do find overtime, this can be increased up to 10% if the case is not severe. Recipes we recommend are usually based around 15%DM and observe progress slowly.
Good lean proteins may include white fish, lean turkey breast, pork tenderloin, venison, kangaroo, rabbit and horse.
Findings hereFats and phytochemicals found in fishoilandolive oilhave been shown to block cellular mechanisms involved in the development of acutepancreatitis, say researchers. Only look to restrict fats if your pet is in an acute phase. Fats are rarely the root cause but excess fatsmay
be problematic in the short term until the animal starts to recover.
Findings hereThere is little need for carbohydrates in the diet, just some nice fresh vegetables, offering colour and variety offering beautiful antioxidants and phytochemicals that are shown to potentially help in pancreatitis. The higher the carbohydrate content, the more likely fat metabolism and absorption will be pushed to one side.
Supplements
Emerging evidence in the health sector, has highlighted nutrient supplementation is key to limit local inflammation and to prevent or manage pancreatitis associated complications.
The immune system is thought to play an important role in the disease pathogenesis of pancreatitis and this is how we focus my approach.Both humans and dogs share the same pathogenosis of pancreatitis so many findings have been interrelated.
Findings hereDigestive enzymes; digestive enzymes such as protease, lipase, cellulose, hemicellulose, amylase and pancreatin are a fantastic addition for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). It takes a load off the pancreas, reducing its activity and thus in turn managing the inflammation.
Findings hereProbiotics; the effects ofL. plantarumhas been evaluated in human trials and the patients who showed attenuated disease severity, improved their intestinal permeability, and had better clinical outcomes in pancreatitis. We do use this probiotic strain and can see a difference in dogs, but research is limited.
Slippery Elm and Glutamine; are best applied in chronic pancreatitis. Slippery elm is regarded as an adaptogenic mucilage that creates a beautiful film around the entire gastrointestinal tract, protecting the immunity epithelial, easing symptoms. Glutamine also helps support gut integrity. Its very important not only supports immunity but also helps release a healthy amount of stomach acid (Hcl), that aids in protein and fat digestion. If gut integrity is poor this may put extra stress on the pancreas.Early studies also points to L-Arginine increasing digestive enzymes.
Findings hereOmega 3 fatty acids (plus tocopherol); contrary to traditional beliefs, studies withomega-3 fish oilhave shown to control inflammatory response and improve the outcome especially in hyper-inflammatory conditions such as pancreatitis. Fish source should be from purer forms such as anchovies or sardines and algae oil where the EPA and DHA fatty acids are provided. There needs to be from as little as 4 10 IU of natural vitamin E added per 1000mg fish oil capsule/liquid to prevent the fish oil from depleting a dogs vitamin E levels and protecting the oil itself from oxidation. Any good omega 3 oil will provide a good source of tocopherol.
Caution should always be taken when supplementing fats to an animal with pancreatitis.Findings herePhenolic and Vitamin C (antioxidants); recent research in phenolics (derived from olives and olive oil) and other antioxidants such as Vitamin C show great potential in protecting tissue and have shown to help the inflammation in pancreatitis.
Phenolics cannot be used in a cats diets.Antioxidant findings hereAshwaganda; during times like this, one should think about reducing stress and inflammation and supporting the endocrine system that is intrinsically linked to the function of the pancreas. Ashwaganda is well known for supporting the stress response and holding court in the endocrine system.
Findings hereMilk thistle; is proven to support liver function, digestion and emulsification of fats via the gallbladder. Looking to support fat digestion and detoxification helps support the pancreas.
Findings hereLifestyle
Reducing stress is probably one of the most effective ways to manage disease. We always suggest looking at your pets emotional profile and ability to cope with stress.
Looking at natural alternatives for flea and worming treatments, titers as opposed to vaccinations and reducing the toxic overload in the household by using natural products are all helpful at approaching this disease holistically.
If your cat or dog is fed a fresh and well balanced diet and not dry food, has reduced toxicity exposure and experiences as little stress as possible, they have the best chance of a healthier outcome. And so therefore, diet, supplements, lifestyle and stress management are the core areas to consider in this disease.
We hope this has been useful and of course, as usual, if you want to check out our services, see the link below.
ConsultationMPN Team x