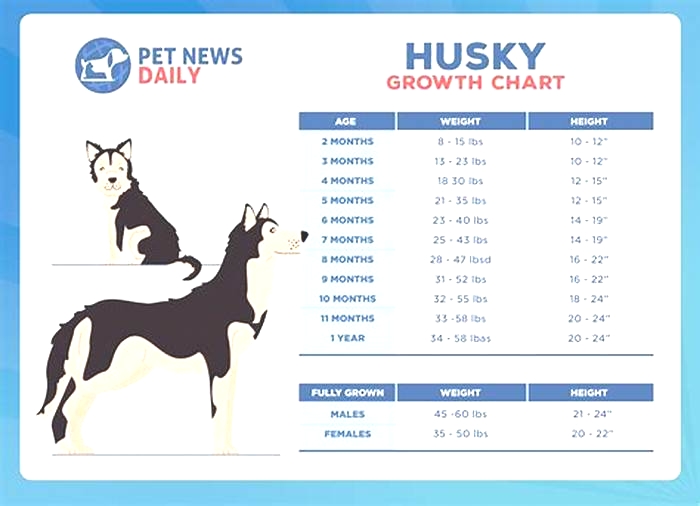
How to tell if a husky is malnourished

What To Feed A Malnourished Dog (4 Steps To Help YOur Pup Recover)
Key Takeaways
- Malnourishment is a serious condition that cant simply be fixed by giving more food to a dog.
- Severely underweight dogs need to be fed a diet high in protein and fat, with frequent small meals and gradually increased calorie density over time.
- Aside from feeding vet-recommended food, dog owners will also have to take him to regular checkups and provide lots of rest and comfort, essentially treating him as a sick dog until he gets back to normal weight.
Malnourishment, whether in humans or animals, is a serious condition that can be difficult to rebound from. This condition of severe weight loss can set in due to a wide range of causes, from a variety of health issues to lack of nutritious food, or even lack of food at all. The basic feeding guidelines I give to pet owners taking care of an emaciated dog goes as follows:
- Choose foods high in fat and protein, as well as minerals such as potassium and phosphates, while being low in carbohydrates.
- Feed the dog six small meals a day so as to not overwhelm their digestive system.
- Administer broad-spectrum vitamins to raise the dogs appetite and general health.
If the condition is severe enough, you may also need to make use of weight gain supplements to help your dogs body regain muscle mass. I tend to recommend these alongside a high-protein and fat recovery diet for rescues from abusive homes, as it helps dogs regain their health that much quicker. Like other experts, I also find that high-quality puppy food contains all of the essential nutrients a malnourished dog needs to get back on their feet. It may be a good idea to start them off on puppy food, and then move on to fresh or homemade food once they can handle more food intake.
What Does Malnourished Mean?
A dog is said to bemalnourishedif it has lost more than 10% of its body weight. You can often look at a dog and tell they are malnourished because it will have ribs sticking out and hip bones protruding.
Malnourished dogsdont only get skinny, they also suffer from severe conditions like dehydration, skin diseases, and lethargy. While malnourishment can have different causes, it most often occurs because of a lack of food or poor quality food.For many, fresh meals for dogs such as those offered by The Farmers Dog and Nom Nom pet food are the answer to dogs nutritional needs.
Ive seen more than my fair share of dog owners having to deal with an underweight dog, because they put the dog on an ill-advised diet instead of vet-recommended pet food that has all the proper nutrients healthy dogs need.
If your dog is malnourished, you need to take it to the vet to determine the cause. The vet will examine the dog and run bloodwork and other tests to find the underlying cause of the malnourishment.
The vet can also give you advice on what kind of diet to feed your emaciated dog. By ruling out any serious health issues, you will know what direction to take to ensure your malnourished dog receives the nutrition it needs.
Your Dog Has a Health Issue
If your dog suffers from a health issue, resolving it will usually quickly lead to improvements in your dogs weight. As the medical condition receives proper care and your dog recovers, his body will soon be able to take in more nutrients, and he will get stronger.
Your Dog Lacks Nutrients
If your dog lacks nutrients because he has not been eating enough food, your approach to helping him get better is going to be extremely important. Some resort to homemade weight gainer for dogs, however, it is essential you do not feed him too much food in the beginning. Your dog can suffer from a condition called refeeding syndrome [1]. If you feed too much at once, your dog could become seriously ill and suffer a dire health crisis.
Critical Steps For Helping Your Dog Recover From Malnutrition
Keeping a healthy dog takes a concerted effort on your part. I have outlined the critical steps below that will help you protect your dogs health and get it back on track. Taking these steps will help protect your dog from suffering from further health issues due to a lack of food or nutrition.
1. Make Sure Your Dog Sees the Vet
One of the most important things you can do to care for your dogs health is to pursue regular vet visits. You should never try to feed your dog without guidance from the vet. The vet can determine the inadequacies of your dogs current diet and help learn how to help your dog put on weight.
Your vet will need to track your dogs health to ensure it is gaining enough weight and having improvements in its health. It is also important for your dogs vital signs to be checked to ensure improvements. Veterinary professionals can help you plan your dogs diet and figure out how much exercise he needs.
2. Provide Warmth and Comfort
Many people do not realize that a malnourished dog is going to need more warmth and comfort than other healthier dogs. Your dog needs a warm and padded place to rest. An emaciated dog does not have ample body fat padding to keep him warm and protect his joints.
Malnourished dogs are also more sensitive to the environment around them. Providing a safe, comfortable, and calming place for your dog to rest will help keep him safe and happy as he recovers.
3. Gradually Increase the Number of Feeding Times
You need to make sure you feed your dog on a specific schedule. Helping your dog gain weight and improve nutrition begins with adding an extra meal each day. Remember that you do not want to go overboard with feeding. Over-feeding can be just as harmful as under-feeding.
By adding an extra meal, instead of increasing the amount fed at each meal, you will help your dog avoid nausea, vomiting, and other digestive health issues that may arise.
It will also prevent overburdening their digestive systems, letting them make efficient use of the nutrients and undergo weight gain at a healthy pace.
4. Improve the Quality of the Dog Food
The quality of your dogs food is essential for improving his malnourishment. If you want to feed your dognutritionally complete homemade dog food, try adding more organ meats because these are full of vitamins and will help increase your dogs weight.
Talk to your vet and determine which food will be best. Some vets recommend that malnourished dogs eat high quality puppy food because it is higher in nutrients and protein.
There are also weight gain supplements available to help dogs get to a healthier size and improve their nutrition intake. Just remember to follow your vets instructions and start gradually. You should work up to the desired amount by slowly increasing the high-protein dog food over a ten-day period until it is at the optimal level.Note that when you get puppy nutrition right in the first place, malnutrition in older dogs can be definitely avoided.
FAQ About Feeding Malnourished Dogs
I am sure you have a lot of questions and concerns about your malnourished dog and how to help induce healthy weight gain. The following are some of the top questions on the subject.
1. How can I help my malnourished dog gain weight?
Before you attempt to feed your dog, take it to the vet for an evaluation. Your vet will tell you how to help yourdog gain weight. You need high-quality, nutrient and calorie-dense foods to help your dog gain weight.
2. How do you revive a malnourished dog?
If a dog is severely malnourished, getting it to the vet right away is essential. Dogs can die of severe malnutrition very quickly. Your dog may need IV treatments and medications. Finding the underlying cause of malnutrition is critical.
3. What is the best food to feed an underweight dog?
Nutrient-dense foods like whole eggs and organ meats can help your dog gain weight. Make sure to ask your vet about any additions to your dogs diet to ensure they are the correct choices.
Malnutrition: Definition, Symptoms and Treatment
Malnutrition refers to getting too little or too much of certain nutrients. It can lead to serious health issues, including stunted growth, eye problems, diabetes, and heart disease.
Malnutrition affects billions of people worldwide. Some populations have a high risk of developing certain types of malnutrition depending on their environment, lifestyle and resources.
This article discusses the types, symptoms and causes of malnutrition and provides information about prevention and treatment.
Malnutrition is a condition that results from nutrient deficiency or overconsumption.
Types of malnutrition include (1,
- Undernutrition: This type of malnutrition results from not getting enough protein, calories or micronutrients. It leads to low weight-for-height (wasting), height-for-age (stunting) and weight-for-age (underweight).
- Overnutrition: Overconsumption of certain nutrients, such as protein, calories or fat, can also lead to malnutrition. This usually results in overweight or obesity.
People who are undernourished often have deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, especially iron, zinc, vitamin A and iodine (
However, micronutrient deficiencies can also occur with overnutrition.
Its possible to be overweight or obese from excessive calorie consumption but not get enough vitamins and minerals at the same time.
Thats because foods that contribute to overnutrition, such as fried and sugary foods, tend to be high in calories and fat but low in other nutrients (4).
SummaryMalnutrition includes undernutrition and overnutrition, both of which can lead to health problems and nutrient deficiencies if not addressed.
The signs and symptoms of malnutrition depend on the type.
Being able to recognize the effects of malnutrition can help people and healthcare providers identify and treat issues related to under- or overnutrition.
Undernutrition
Undernutrition typically results from not getting enough nutrients in your diet.
This can cause (5):
- Weight loss
- Loss of fat and muscle mass
- Hollow cheeks and sunken eyes
- A swollen stomach
- Dry hair and skin
- Delayed wound healing
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Depression and anxiety
People with undernutrition may have one or several of these symptoms. Some types of undernutrition have signature effects.
Kwashiorkor, a severe protein deficiency, causes fluid retention and a protruding abdomen. On the other hand, the condition marasmus, which results from severe calorie deficiency, leads to wasting and significant fat and muscle loss (5).
Undernutrition can also result in micronutrient deficiencies. Some of the most common deficiencies and their symptoms include (
- Vitamin A: Dry eyes, night blindness, increased risk of infection (
6 ). - Zinc: Loss of appetite, stunted growth, delayed healing of wounds, hair loss, diarrhea (
7 ). - Iron: Impaired brain function, issues with regulating body temperature, stomach problems (
8 ). - Iodine: Enlarged thyroid glands (goiters), decreased production of thyroid hormone, growth and development issues (
9 ).
Since undernutrition leads to serious physical issues and health problems, it can increase your risk of death.
In fact, its estimated that stunting, wasting and zinc and vitamin A deficiencies contributed to up to 45% of all child deaths in 2011 (
Overnutrition
The main signs of overnutrition are overweight and obesity, but it can also lead to nutrient deficiencies.
Research shows that people who are overweight or obese are more likely to have inadequate intakes and low blood levels of certain vitamins and minerals compared to those who are at a normal weight (
One study in 285 adolescents found that blood levels of vitamins A and E in obese people were 210% lower than those of normal-weight participants (
This is likely because overweight and obesity can result from an overconsumption of fast and processed foods that are high in calories and fat but low in other nutrients (
A study in over 17,000 adults and children found that those who ate fast food had significantly lower intakes of vitamins A and C and higher calorie, fat and sodium consumption than those who abstained from this type of food (
Assessing Malnutrition
Symptoms of malnutrition are assessed by healthcare providers when they screen for the condition.
Tools that are used to identify malnutrition include weight loss and body mass index (BMI) charts, blood tests for micronutrient status and physical exams (
If you have a history of weight loss and other symptoms associated with undernutrition, your doctor may order additional tests to identify micronutrient deficiencies.
Identifying nutrient deficiencies that result from overnutrition, on the other hand, can be more difficult.
If youre overweight or obese and eat mostly processed and fast foods, you may not get enough vitamins or minerals. To find out if you have nutrients deficiencies, consider discussing your dietary habits with your doctor.
SummarySymptoms of undernutrition include weight loss, fatigue, irritability and micronutrient deficiencies. Overnutrition can result in overweight, obesity and a lower intake of certain vitamins and minerals.
Malnutrition can lead to the development of diseases and chronic health conditions.
Long-term effects of undernutrition include a higher risk of obesity, heart disease and diabetes (
One study in 50 adolescents in Brazil found that boys who had stunted growth as a result of undernutrition early in life gained 5% more fat mass over three years compared to their peers who did not have stunting (
Additional research found that 21% of adolescents with stunted growth in Brazil had high blood pressure compared to less than 10% of adolescents without stunting (
Researchers suspect that childhood undernutrition causes changes in metabolism that may lead to a higher likelihood of developing chronic diseases later in life (
Overnutrition can also contribute to the development of certain health issues.
Specifically, overweight or obese children have a higher chance of heart disease and type 2 diabetes (
A study in over 369,000 children found that those who were obese were more than four times as likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to their peers who had a normal BMI (
Since the long-term effects of malnutrition can increase your risk of certain diseases, preventing and treating malnutrition may help reduce the prevalence of chronic health conditions.
SummaryResearch has linked undernutrition in childhood with a higher risk of developing high blood pressure and obesity later in life. Overnutrition may also increase your likelihood of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Malnutrition is a worldwide problem that can result from environmental, economic and medical conditions.
The WHO estimates that over 460 million adults and 150 million children are undernourished, while more than two billion adults and children are overweight or obese (
Common causes of malnutrition include:
- Food insecurity or a lack of access to sufficient and affordable food: Studies link food insecurity in both developing and developed nations to malnutrition (
28 ,29 ,30 ). - Digestive problems and issues with nutrient absorption: Conditions that cause malabsorption, such as Crohns disease, celiac disease and bacterial overgrowth in the intestines, can cause malnutrition (
31 ,32 ,33 ). - Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use can lead to inadequate intake of protein, calories and micronutrients (
34 , 35). - Mental health disorders: Depression and other mental health conditions can increase malnutrition risk. One study found that the prevalence of malnutrition was 4% higher in people with depression compared to healthy individuals (
36 ). - Inability to obtain and prepare foods: Studies have identified being frail, having poor mobility and lacking muscle strength as risk factors for malnutrition. These issues impair food preparation skills (
37 ,38 ).
SummaryCauses of malnutrition include food insecurity, certain health conditions and mobility issues.
Malnutrition affects people in all parts of the world, but some populations are at a higher risk.
Populations that are prone to malnutrition include:
- People living in developing countries or areas with limited access to food: Undernutrition and micronutrient deficiencies are especially common in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia (
10 ,39 ). - Individuals with increased nutrient needs, especially children and pregnant or breastfeeding women: In some developing countries, 2431% of pregnant and breastfeeding mothers are malnourished (40, 41).
- People that live in poverty or have low incomes: Low socioeconomic status is associated with malnutrition (
42 ). - Older adults, particularly those who live alone or have disabilities: Research shows that up to 22% of older adults are malnourished and over 45% are at risk of malnutrition (
43 ,44 ). - People with issues that affect nutrient absorption: People with Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis may be up to four times more likely to have malnutrition than those without these conditions (
32 ,33 ).
SummaryOlder individuals, people living in poverty and those with digestive problems or an increased nutrient need are at high risk of malnutrition.
Preventing and treating malnutrition involves addressing the underlying causes.
Government agencies, independent organizations and schools can play a role in preventing malnutrition.
Research suggests that some of the most effective ways to prevent malnutrition include providing iron, zinc and iodine pills, food supplements and nutrition education to populations at risk of undernutrition (
In addition, interventions that encourage healthy food choices and physical activity for children and adults at risk of overnutrition may help prevent overweight and obesity (
You can also help prevent malnutrition by eating a diet with a variety of foods that include enough carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water.
Treating malnutrition, on the other hand, often involves more individualized approaches.
If you suspect that you or someone you know is undernourished, talk to a doctor as soon as possible.
A healthcare provider can assess the signs and symptoms of undernutrition and recommend interventions, such as working with a dietitian to develop a feeding schedule that may include supplements.
SummaryInterventions that encourage a healthy lifestyle or provide nutrition education and supplements may help decrease the prevalence of malnutrition. Treatment usually involves assessment by a doctor and recommendations from a dietitian.
Malnutrition refers to overnutrition and undernutrition.
People who are undernourished may experience weight loss, fatigue and mood changes or develop vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Overnutrition can lead to overweight, obesity and inadequate micronutrient intakes and deficiencies.
Both types can lead to health issues if not addressed.
If you believe that you or someone you know may be malnourished, especially undernourished, talk to a doctor as soon as possible.