How can pet obesity be fixed
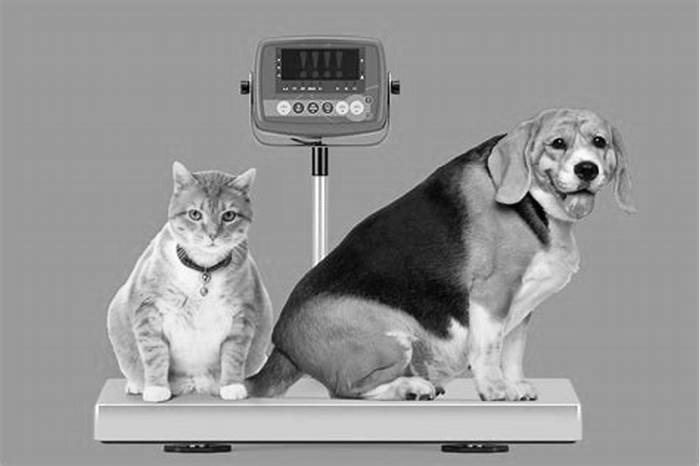
Obesity in Dogs: What to Know
According to the Association for Pet Obesity Prevention, more than half of all dogs are overweight or obese. A dog is considered overweight when their weight is 15% or more above the ideal. Dogs are obese when their weight is 30% or more above the ideal weight for that animal.
Generally, obesity in dogs occurs when there is an imbalance between the amount of energy consumed versus the amount of energy used, although studies show that other factors can also contribute to the problem. Obese dogs tend to be older, female, and spayed. As one might expect, obese dogs tend to receive less exercise than their healthy-weight counterparts.
According to one study, some breeds have shown a predisposition to obesity. The breeds in question include Basset Hounds, Dachshunds, Beagles, Cairn Terriers, West Highland White Terriers, Scottish Terriers, Shetland Sheepdogs, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels, Cocker Spaniels, and Labrador Retrievers. In contrast, the studys authors note, some breeds, such as the sighthounds, rarely develop obesity.
Dogs that have been spayed or neutered also may have a greater tendency to gain weight, possibly due to the change in metabolism and loss of hormones. Its important for dog owners to be aware of this possibility and make certain their dogs maintain a healthy weight after surgery.
Age can also be a factor in obesity. As dogs age, their activity level decreases and they lose lean body mass. Dog owners should work with their veterinarians to adjust food intake as the dog ages.
Obesity in Dogs and Health Issues
Unfortunately, obesity can contribute to (or cause) serious health problems in dogs. Among the health problems that are made worse by obesity are:
Obesity has also been shown to contribute to an overall shorter life span for dogs when compared to the lifespan of healthy-weight dogs.
Is My Dog Obese?
Dog owners can access a variety of resources to determine if their pet is obese. Online, they can look for body condition charts from responsible sources to get a visual idea of how their dog should be shaped. Generally, dogs with an ideal weight are well-proportioned. You should be able to easily feel their rib bones, spine, and pelvic bones, but they should not be visible or protruding. There should be a visible tuck at their waist.
Of course, the best way to tell if your dog is overweight or obese is for them to receive regular check-ups from their veterinarian. Your dogs veterinarian is able to determine the animals ideal weight and provide you with a plan for reaching that ideal weight if the animal is overweight, obese, or underweight.
Helping Your Dog Lose Weight Safely
Just like with people, its important that dog owners have a healthy plan to reduce their dogs weight if the animal is overweight or obese. They should consult with their veterinarian to determine how to best decrease the animals caloric intake and increase exercise and activities.
This is likely to be a long-term project that will be most successful with regular monitoring and adjustments to diet and exercise. Today, there are even foods designed to help dogs lose weight. Again, your veterinarian can help determine the best approach for your dog.
Its important that exercise programs be started slowly and increased gradually. Walking, playing fetch with a ball, and socializing at dog parks are good, low-impact ways for dogs to increase canine activity levels. You can also try getting involved with AKC FIT DOG, which will get both you and your dog moving. As your dog becomes more used to the activity, you can slowly increase the amount of time you and your dog are doing the activity.
The one thing pet owners want to be sure to avoid is yo-yo dieting. Repeated gaining and losing weight is not healthy for the animal and can lead to other health problems.
An active dog at a healthy weight will be a happier and healthier dog and will likely have a longer life to share with their human family.
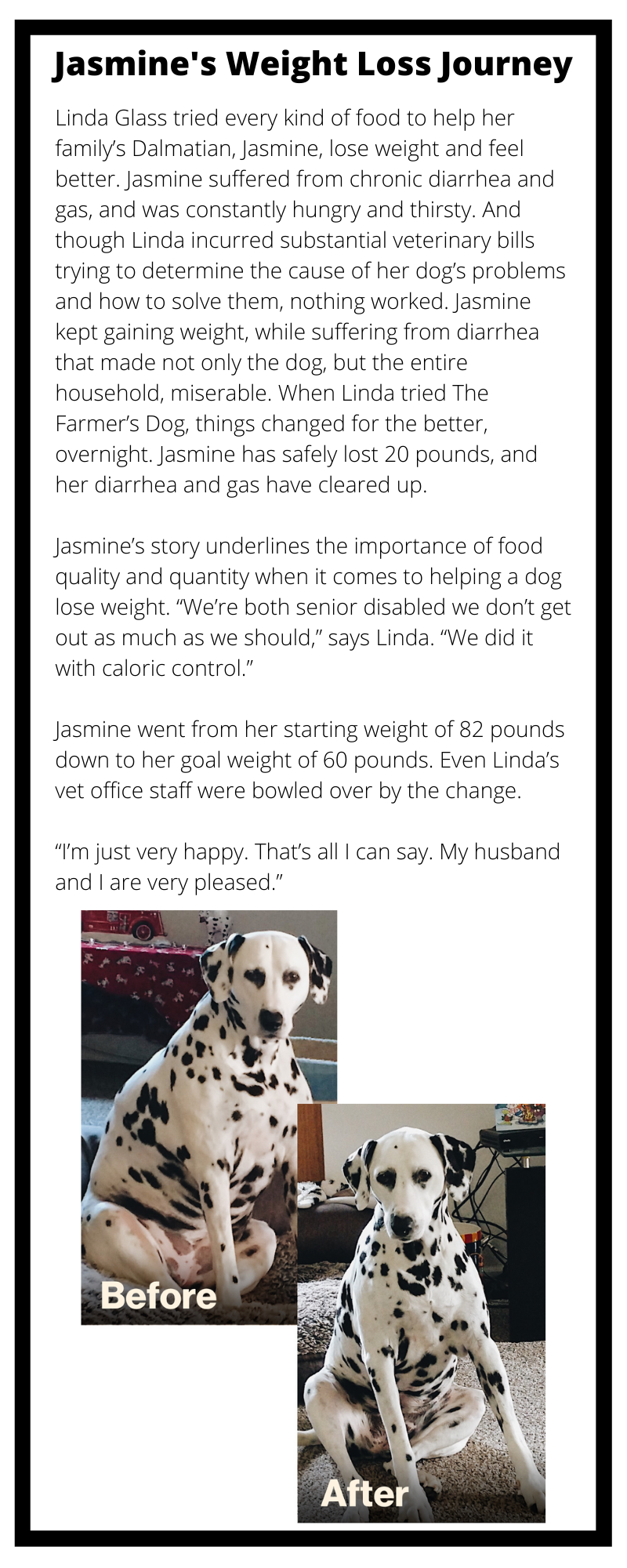
Obesity in Dogs: A Major Health Threat Hiding in Plain Sight
This Is a Paid Advertisement for The Farmers Dog
Theres a weight problem in America and it isnt just affecting humans.
The most recent statistics classify the majority of dogs in the U.S.56%as overweight or obese. While that makes obesity a major health crisis for dogs, its a problem thats often overlooked, as many pet owners may not even realize their pets are overweight.
I see people coming in constantly with 90-pound Labs and they say, she looks great, says Dr. Ernie Ward, DVM, CVFT, and founder of theAssociation for Pet Obesity Prevention(APOP). Well, actually, that dog is 15 pounds overweight. But weve normalized it. This kind of dog embodies what APOP has called the fat pet gapthe misalignment between what we think a dog should look like and what a healthy body composition should really be.
Obesity in dogs comes with significant consequences. In fact, Ward and other vets call it our pets biggest health threat. And its not an isolated issue; obesity is linked to a whole raft of health problems including arthritis, chronic kidney disease, bladder/urinary tract disease, liver disease, low thyroid hormone production, diabetes, heart failure, high blood pressure, and cancer. We think its very important that people understand this isnt just a cosmetic issue, says Dr. Ward. There is a physiological consequence to this.
A slimmer margin of error
While obesity is loosely defined as 30% above ideal body weight (there is no universally accepted definition forpets), veterinary experts say just being overweight impacts pet health. And thats one of the challenges in addressing this issuemany pet owners may simply not realize thereisan issue.
You look at your dog and it seems healthy and its active and doesnt have any apparent health issues, says Ward. So you say, its normal, and by extension its morphology, or its size, is normal. But the problem is that we often dont know what what normal is when it comes to dogs, so we project our own human-centric perspective. In human terms, we think we just need to drop five pounds, says Ward. Well, the amount of physiological impact of a few pounds is much, much greater and more concentrated in pets than in people. Five pounds on a cat is catastrophic. Five pounds on a Lab is significant. We think a few pounds off my Lab; what could the consequence of that be..? But the consequences are that Labs hips are deteriorating, its causing damage to the kidneys, its probably causing high blood pressure which is causing a constellation of problems, and its increasing cancer risk.

Dr. Carol Osborne, an integrative veterinarian at Chagrin Falls Pet Clinic in Ohio, echoes the fact that a dog doesnt have to be clinically obese to experience health consequences. Being just 10% overweight decreases a dogs lifespan by one-third and predisposes him to heart, kidney and liver disease as well as diabetes, arthritis,and cancer, she says.
Osborne says that adipose tissue (aka fat) is filled with blood vessels, and the added rich blood creates inflammation. This all creates an environment attractive to cancer cells and increases a dogs risk of developing the disease, she says.
Cancer is the number one killer of dogs today, says Osborne.
And, for some smaller breeds, extra pounds make a huge difference. Three extra pounds for canines in the toy category is the equivalent of gaining approximately 30 pounds for you or me, she says.
Holistic veterinarian and researcher Dr. Jean Dodds, of Hemopet veterinary center in California, says the health effects of having even a marginally overweight dog include reduced energy with resultant less exercise, easy keeper (gains weight on small amounts of food), skin and hair coat conditions, and irregular female reproductive cycles, if intact.
Conversely, obese dogs may benefit from even just slight weight loss. According to aclinical trial published in 2010,obese dogs with osteoarthritis showed a significant decrease in lameness from weight loss starting at 6.10%.
Another study,published in the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine in 2018 found that being overweight was associated with a shorter lifespan in the 12 dog breeds studied. The estimated reduction in lifespan for the overweight group was up to two-and-a-half years.
We look at a dog with obesity and if a dog loses as little as 6% body weightthats six pounds on a 100-pound Retrieverit makes a difference, says Ward. It doesnt take a lot of weight loss to make the pet feel better. I really try to emphasize that when Im talking to (pet owners) because its a quality of life issue as much as a longevity and disease-prevention issue.
Osborne says shes seen this quality of life improvement from weight loss time and again. One of her clients came in with a two-year-old male Pomeranian named Smokey that weighed in at 45 pounds. When he first visited, the dog already had one cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) surgery on a hind leg and was about to have a second. Osborne changed his dietwhich involved stopping the dry kibble and replacing it with chicken and fresh vegetables.
At this point he is down to 22 pounds, she says. He acts, feels and looks like a puppy instead of sleeping under the kitchen table most of the day and barely moving at all. Hes running around the house, ready to play and having a ball. And he wont need another surgery after all.
Rewriting your dogs future
For pet owners with dogs who are not obese and who arent showing obvious health symptoms, the concern may not seem as pressing. But Ward warns against not taking action when you can.
I see too often a 10-year-old Lab mix and suddenly they cant get into the car because of crippling hip arthritis caused by obesity, he says. But if you can rewind the tape, you dont have the years of cumulative damage. (Obesity) is a slow and insidious and silent killer, and people may know its happening, but they dont take action until theres a crisis. I say that nobody treats obesity until theres a catastrophe. And when its catastrophic, you may not recover.
A guide for dog owners: How to assess your dogs weight
The question remains: How can pet owners determine the ideal weight for their dogs?
The rib testOsborne says it begins with keeping regular track of your dogs body condition. She recommended the rib test.
Stand behind your dog, gently run your hands along either side of the rib cage, she says. You should be able to easily feel, but not see each rib, and your dog should have a waist or a tucked up area in front of the hind legs. If you can pinch more than an inch and/or your dog has lost his waist, its probably time to think about reducing.
The standing testWard opts for another method. I recommend you do the standing test. Look at the dog from the sidelean down and look from the sideand see [if] their abdomen or stomach is sagging, he says. Then I look from the top: From standing I should see an hourglass indentation in front of the hips. You should see the chest extend out and the waist tapers in making an hourglass.
While dogs vary widely in body shape and volume of hair and fur, Ward says this test should work for 95% of dogs (he notes that exceptions include English Bulldogs and Pugs).
Food matters most
Many vets agree that weight loss begins and ends at the food bowl for dogs and cats. Based on available literature and experience, Ward breaks down the weight-loss math this way: 60-70% diet and 30-40% exercise.
So, knowing exactly how much to feed your dog becomes key. Like many experts, Ward cautions against using the guidelines on most commercial dry dog food packages to determine how much youre feeding. The parameters, which are based on adult dogs for all life stages, are far too broad to accommodate every dogs needs. For example, Ward says, spaying or neutering a dog reduces their energy requirement by 20-30%. So already, if youre feeding according to guidelines youre overfeeding a pet who is spayed or neutered, he says. I see so many pet owners say Im feeding exactly what they say on the bag, and its like no, thats too much.
Its a good idea to work with your vet to assess your dogs body condition, muscle condition, lifestyle and any concurrent medical conditions and determine how many calories you should be feeding.
You can also consult the tools available online(including on APOPs site)which provide a good estimate of weight ranges and caloric needs by breed and size.
As to food quality, Osborne recommends fresh food including lean protein like chicken, turkey, fish, eggs and tofu, and fiber through fresh vegetables such as Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, cabbage and spinach.
While some dog owners hesitate around the idea of feeding people food, this kind of real, fresh food is more nutrient-dense, and more bioavailable than dried, processed food. Those planning to prepare fresh food at home for any length of time should be sure to consult their vet to ensure meals are correctly balanced and contain the necessary vitamins and nutrients.Subscribing to a fresh-food plan makes it easier, and safer, to feed nutritionally balanced meals.
While food is the biggest factor, pet owners should also plan to exercise dogs for a minimum of 20 minutes, twice a day. And be careful with snacks. You can use fresh veggies as healthy treats and avoid processed mystery-ingredient treats and things like pig ears, and bully sticks.
If you dont eat it, neither should your dog, Osborne says.











